
Subscribe for Free!
Join our newsletter to explore innovative sustainability initiatives, eco-friendly tips, and impactful activities

Join our newsletter to explore innovative sustainability initiatives, eco-friendly tips, and impactful activities
How Artificial Intelligence can benefit Sustainability
June 8, 2024
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in achieving a sustainable future. This technology transforms various economic sectors by helping manage environmental impacts and climate change. This article explores how AI optimizes renewable energy, promotes precision agriculture, improves supply chains, and aids in disaster prediction and response. We will also examine the benefits and challenges of AI for sustainability, highlighting concrete examples and the ethical considerations associated with its use.
AI is a key catalyst in transforming the renewable energy sector. Advanced algorithms, for example, allow for optimizing energy grids by more efficiently integrating solar and wind energy into electric networks. This optimization reduces energy losses and increases the reliability of energy systems.
In agriculture, AI promotes precision agriculture, a method that allows for more efficient management of resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. Systems like those from John Deere use AI to analyze weather conditions and soil, enabling farmers to optimize resource use and increase yields while reducing environmental impact.
AI is not limited to renewable energy and agriculture. It is also used to create sustainable supply chains by optimizing transportation routes to reduce carbon emissions. For instance, UPS uses AI algorithms to plan the most efficient delivery routes, saving millions of liters of fuel each year. Additionally, AI helps monitor the environment and predict natural disasters, such as floods and wildfires, saving lives and minimizing damage.
One of the major benefits of AI is job creation. According to some studies, AI could generate 38.2 million new skilled jobs, thus stimulating the global economy. Moreover, AI improves the management of natural resources and contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, aligning economic practices with sustainable development goals.
However, the adoption of AI is not without challenges. The increased energy consumption of data centers and deep learning algorithms poses ecological problems. For instance, training a single language model can generate as much CO2 as five cars over their lifetime. Therefore, it is essential to develop more sustainable AI solutions, focusing on balancing hardware and software, and improving the energy efficiency of algorithms.
AI plays a crucial role in conserving biodiversity. For example, the organization WildTrack uses machine learning algorithms to analyze animal footprints. This non-invasive method allows monitoring populations of endangered species without disturbing them. Thanks to AI, biologists can identify species, estimate population sizes, and track animal movements with remarkable precision.
Another example is the project by the University of Copenhagen, which uses drones equipped with cameras and sensors to monitor wildlife in hard-to-reach areas. The images captured are then analyzed by AI models to detect and identify animals, enabling continuous and precise biodiversity monitoring.
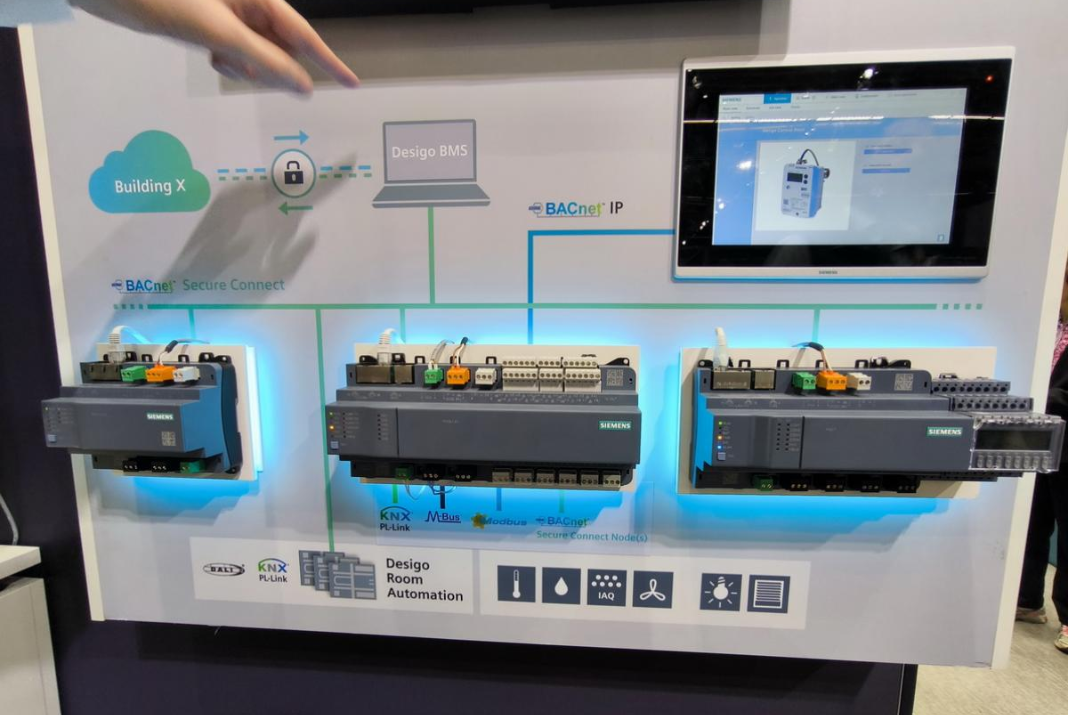
Buildings account for a significant portion of global energy consumption. AI enables optimizing energy management in buildings, reducing electricity consumption and carbon emissions. For instance, Siemens has developed an AI-based energy management system that monitors and controls heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
This system analyzes real-time data to identify energy inefficiencies and automatically adjusts settings to optimize energy consumption.
Moreover, companies like Google use AI to reduce energy consumption in their data centers. In 2016, Google started using DeepMind AI to manage the cooling of its data centers, reducing energy consumption by 40% in these facilities. These substantial savings show how AI can contribute to more sustainable energy management practices.
Precision agriculture is another area where AI can have a significant impact by optimizing the use of agricultural resources. The startup Climate Corporation uses weather data, soil analyses, and satellite images to provide farmers with specific recommendations for each plot. This information allows farmers to adjust irrigation, fertilization, and crop management based on local conditions, reducing resource waste and environmental impacts while increasing productivity.
Another example is the AI system developed by IBM, Watson Decision Platform for Agriculture, which integrates sensor data, satellite images, and weather forecasts to help farmers make informed decisions. This system can, for example, predict crop yields, detect diseases at an early stage, and recommend specific actions to improve plant health and maximize yields.
AI is also used to improve waste management and recycling processes. For example, AMP Robotics has developed AI-powered robots that can sort recyclable materials with much higher precision and speed than traditional methods. These
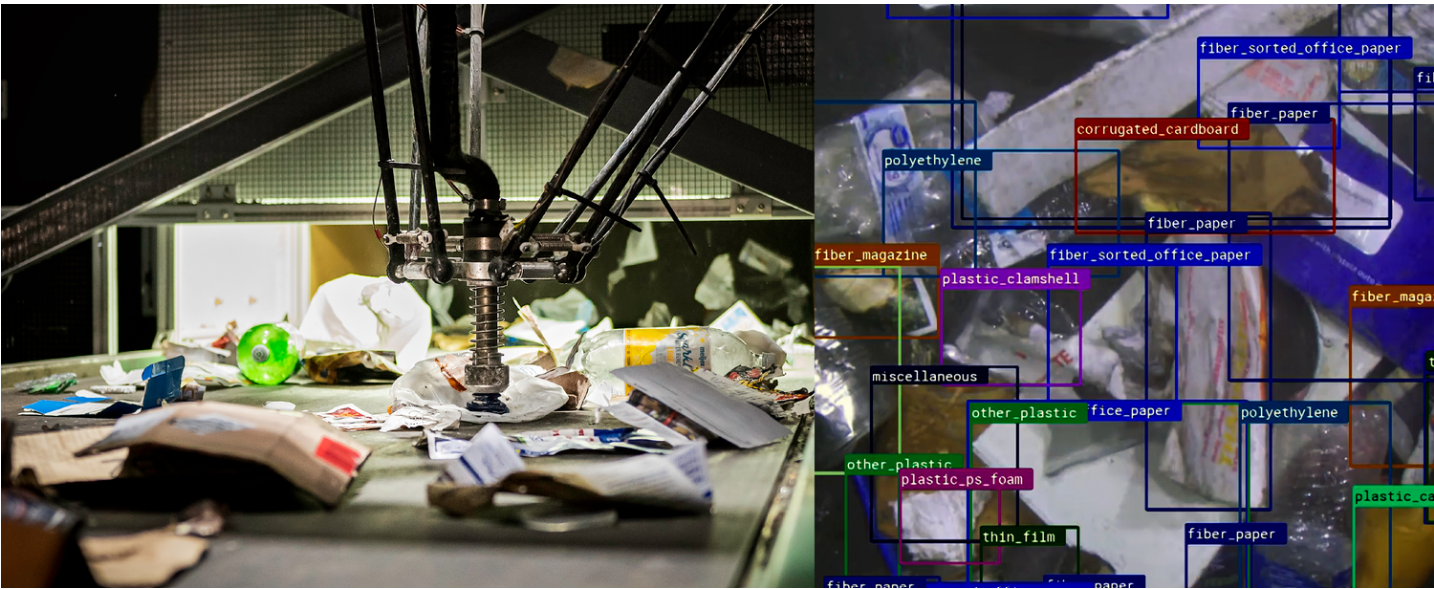

robots use cameras and sensors to identify materials and sort them by type, increasing the efficiency of recycling centers and reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
In Europe, the "AI-Waste" project uses machine learning algorithms to optimize waste collection in cities. Garbage trucks equipped with sensors collect data on the fill levels of trash bins, allowing algorithms to optimize collection routes to reduce CO2 emissions and operational costs.
Environmental monitoring is essential for protecting our planet, and AI offers powerful tools for this task. For instance, researchers use AI models to analyze satellite images and detect environmental changes, such as deforestation, water pollution, and glacier movements. These analyses enable continuous, large-scale monitoring, providing crucial data for environmental policy and conservation decision-making.
The European Space Agency (ESA) uses AI to analyze data from its Sentinel satellites, which monitor the Earth's surface and oceans. AI algorithms quickly detect environmental changes, such as oil spills, wildfires, and floods, and alert relevant authorities for a swift and effective response.
These concrete examples show that AI is a powerful tool for promoting sustainability in various fields. From preserving biodiversity to optimizing energy in buildings, precision agriculture, waste management, and environmental monitoring, AI offers innovative solutions to address the environmental challenges of our time.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence is an essential driving force for a sustainable future. Its potential to optimize renewable energy, promote precision agriculture, and improve supply chains and natural disaster management is immense. However, to fully realize these benefits, it is necessary to overcome challenges related to energy consumption and carbon emissions, and to adopt ethical and responsible practices.
#AI #Sustainability #RenewableEnergy #PrecisionAgriculture #DisasterManagement #Environment