
Subscribe for Free!
Unlock Expert Advice, Event Invitations, and Premium Content

Unlock Expert Advice, Event Invitations, and Premium Content
Mycorrhizae, an Innovative Solution for Agriculture
May 24, 2022

What are Mycorrhizae?
Mycorrhizae, an essential asset for sustainable agriculture, are beneficial symbiotic relationships established between plant roots and certain soil fungi. They involve over 95% of terrestrial plants, most of which are agricultural and horticultural plants.
Mycorrhization is indispensable for 80% of rooted plants. These symbiotic relationships promote the absorption of mineral elements from the rhizosphere and soil by the roots, thereby improving the nutrition of most plant species. They also enhance water absorption and resistance to water stress and diseases, facilitating the development of other microorganisms necessary for tree growth and soil balance.
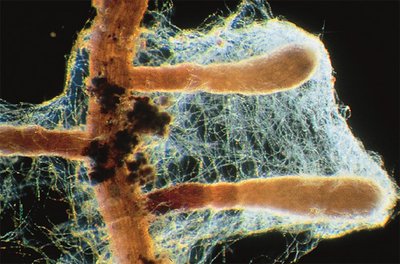
Different Types of Mycorrhizae:
There are seven forms of mycorrhizal associations, but we will focus on three: Ectomycorrhizae, Endomycorrhizae (or arbuscular mycorrhizae), and Ectendomycorrhizae, as they are the most common and studied types, particularly for their roles in agriculture and forestry.
The fungi develop mainly around the root, forming a mycelial sleeve, or mantle, from which hyphae (the filament that forms the mycelium of higher fungi and lichens) develop and are inserted between the cortical cells of the root (Hartig's network), the mycelial cells never penetrating the plant cells.
This type of association is mainly found in forest trees in temperate, Mediterranean and boreal regions, but has also been described in some tropical species of the Dipterocarpaceae, Euphorbiaceae and other families.
Characterized by the absence of an external mycelial sheath and the penetration of fungal hyphae into cortical cells. These intracellular hyphae extensively branch within the root cortex cells to form structures called arbuscules.
This symbiosis is encountered in nearly 80% of plants, including the majority of cultivated plants (fruit and ornamental trees, cereals, aromatic plants, etc.).
Characterized by the presence of both the mycelial sheath and the development of inter- and intracellular hyphae. They are found in the Ericaceae and Monotropaceae families and are formed by Basidiomycetes.

Solutions to Facilitate Mycorrhizal Exploitation:
In agriculture, exploiting mycorrhizae has become challenging due to decreasing and simplifying rotations, excessive use of synthetic chemical inputs, and increasing cultivation of varieties resistant to mycorrhizal fungi. However, various measures are already possible to respect and promote this beneficial association:
Overall, mycorrhization allows plants to compensate for their lack of mobility and shallow rooting. Mycorrhizal fungi are not toxic to plants in case of overdosing; they can expand the root's exploration area and absorb more nutrients. Therefore, the use of biocides should be avoided.
The BioScience Club is a scientific club at the Faculty of Biological Sciences at the University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene, founded in 2017. It continues the legacy of one of Algeria's first student clubs, named ORCHIDÉE in 1989.
The club aims to popularize biological sciences by organizing awareness events, competitions, educational outings, panels, and conferences, promoting exchanges among students and helping them express their creativity and innovation.
Article Written by BioScience Club, Partner of the Foodtech Startup Challenge 2022.
For more information, visit: